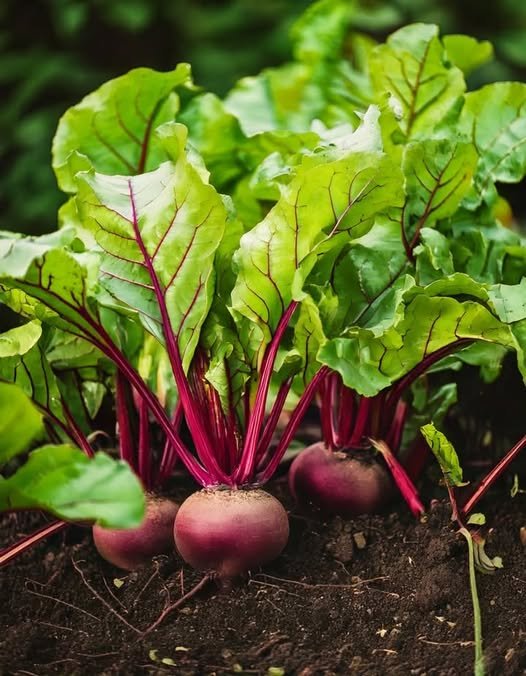
Growing your own beets can be a rewarding endeavor, providing you with fresh, nutritious produce right from your garden. Beets are a versatile crop, known for their sweet, earthy flavor and vibrant color. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a healthy addition to any diet. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or a beginner, cultivating beets can be a straightforward process if you follow some essential guidelines. This article will guide you through the steps to ensure a flourishing beet harvest, allowing you to skip purchasing them from the store and enjoy the fruits of your labor.
Selecting the Right Beet Varieties
Choosing the right beet variety is crucial for a successful harvest. There are several types of beets, each with unique characteristics. For example, ‘Detroit Dark Red’ is a popular variety known for its deep red color and sweet flavor, while ‘Golden Beet’ offers a milder taste and a striking yellow hue. If you’re looking for something unique, consider ‘Chioggia’ beets, which have a distinctive candy-striped interior. When selecting varieties, consider your climate, soil type, and personal taste preferences. Mixing different varieties can also add diversity to your garden and culinary options.
Preparing the Soil for Optimal Growth
Beets thrive in well-drained, loamy soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. Before planting, it’s essential to prepare your soil by removing any rocks or debris and breaking up large clumps. Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil fertility and structure. Beets are sensitive to acidic soils, so if necessary, adjust the pH by adding lime. A soil test can help determine the nutrient levels and pH, allowing you to make informed amendments. Proper soil preparation will set the foundation for healthy beet growth.
Timing Your Planting for Maximum Yield
Timing is critical when planting beets. They are a cool-season crop, best sown in early spring or late summer for a fall harvest. In regions with mild winters, beets can be grown almost year-round. The key is to avoid the hottest part of the summer, as high temperatures can cause beets to bolt or develop poor flavor. Sow seeds directly into the garden when the soil temperature is at least 50°F (10°C). Stagger planting every two to three weeks to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season.
Ensuring Proper Spacing and Depth
Proper spacing and planting depth are essential for beet development. Sow beet seeds about 1/2 inch deep and 1 to 2 inches apart in rows that are 12 to 18 inches apart. Beets need space to develop their roots, so thinning is necessary once seedlings are a few inches tall. Thin to about 3 to 4 inches apart to allow room for the roots to grow. Crowded plants can lead to smaller, misshapen beets and increased competition for nutrients.
Watering Techniques for Healthy Beets
Consistent moisture is vital for beet growth, but overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues. Aim to provide about 1 inch of water per week, either from rainfall or supplemental irrigation. Water deeply and infrequently to encourage deep root development. Mulching around the plants can help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature. Beets are particularly sensitive to drought during the early stages of growth, so ensure they receive adequate moisture during this critical period.
Fertilizing Strategies for Nutrient-Rich Soil
Beets require a balanced supply of nutrients to thrive. Before planting, incorporate a balanced fertilizer or organic amendments like compost into the soil. Avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers, as they can promote excessive leaf growth at the expense of root development. A side dressing of a balanced fertilizer or compost tea midway through the growing season can provide an additional nutrient boost. Monitor plant growth and adjust fertilization as needed, based on the appearance of the foliage and overall plant health.
Managing Pests and Diseases Effectively
Beets can be susceptible to various pests and diseases, such as leaf miners, aphids, and fungal infections. Regularly inspect plants for signs of damage or disease, and take action promptly. Use floating row covers to protect young plants from pests, and encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs to help control aphid populations. Practice crop rotation and remove any diseased plant material to prevent the spread of pathogens. Maintaining healthy soil and proper plant spacing can also reduce the risk of pest and disease issues.
Companion Planting for Beets
Companion planting can enhance beet growth and deter pests. Plant beets alongside onions, garlic, or bush beans, which can help repel pests and improve soil health. Avoid planting beets near pole beans or field mustard, as they can compete for nutrients or attract harmful insects. Marigolds and nasturtiums are excellent companion plants that can attract beneficial insects and deter pests. Strategic companion planting can lead to healthier plants and a more productive garden.
Harvesting Beets at the Right Time
Harvesting beets at the right time ensures optimal flavor and texture. Beets are typically ready to harvest 50 to 70 days after planting, depending on the variety. The best time to harvest is when the roots are 1.5 to 3 inches in diameter. Larger beets can become woody and lose their sweetness. Gently loosen the soil around the roots and pull them out by the tops. If you plan to store beets, leave about an inch of the greens attached to prevent bleeding.
Storing Harvested Beets for Longevity
Proper storage is key to extending the shelf life of your harvested beets. Remove the greens, leaving a small portion of the stems attached, and store them separately. Beets can be stored in a cool, dark place with high humidity, such as a root cellar or refrigerator crisper drawer. Place them in a perforated plastic bag or a container with damp sand to maintain moisture. Stored correctly, beets can last for several months, allowing you to enjoy your harvest well into the winter.
Conclusion and Final Tips for a Successful Beet Harvest
Growing beets can be a fulfilling experience, providing you with fresh, homegrown produce. By selecting the right varieties, preparing the soil, and following proper planting and care techniques, you can achieve a bountiful harvest. Pay attention to the needs of your plants, from watering and fertilizing to pest management and companion planting. With these tips, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying a successful beet harvest, saving money, and savoring the taste of homegrown goodness. Remember, gardening is a journey of learning and adaptation, so don’t be afraid to experiment and adjust your methods as needed.