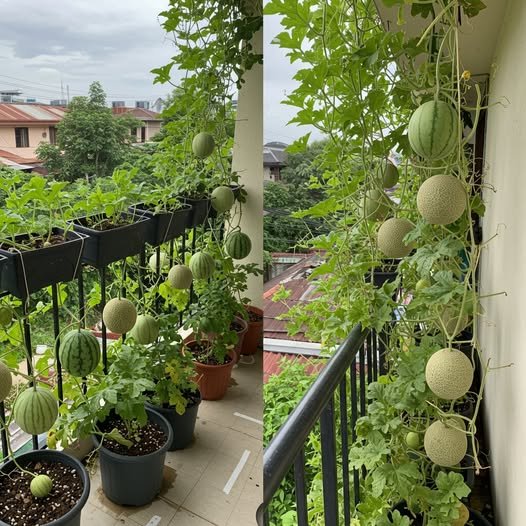
Secrets to Growing Melons with Abundant Fruits – Must-Know Tips!
Melons are a favorite summer fruit, loved for their refreshing sweetness and high water content. But many gardeners struggle to get their melon plants to produce an abundance of fruits. The secret lies in proper care, pollination techniques, soil preparation, and maintenance. Follow these essential tips to maximize your melon harvest and enjoy a plentiful supply of homegrown, juicy melons.
1. Choosing the Best Melon Varieties for High Yield
Not all melons are equally productive. Some varieties naturally produce more fruit than others. Choosing the right variety can make a significant difference in your harvest.
Top High-Yield Melon Varieties:
- Cantaloupe (Hale’s Best, Ambrosia): Sweet and aromatic with heavy yields.
- Watermelon (Sugar Baby, Crimson Sweet): Compact, high-producing vines.
- Honeydew (Green Flesh, Golden Honeydew): Thrives in warm climates and yields multiple fruits per vine.
- Galia Melon: A hybrid variety known for abundant production and rich flavor.
- Canary Melon: Produces consistently large fruits with a bright yellow skin.
2. Preparing the Best Soil for Melons
Melons require nutrient-rich, well-draining soil to support fast growth and high fruit yield.
Ideal Soil Composition:
- 40% Loamy Garden Soil – Provides essential minerals and structure.
- 30% Aged Compost or Manure – Boosts fertility for better fruiting.
- 20% Sand or Perlite – Ensures proper drainage and prevents root rot.
- 10% Coco Peat or Peat Moss – Helps retain moisture without overwatering.
- Optimal pH: Maintain a soil pH of 6.0-6.8 for maximum nutrient uptake.
3. Planting Melons for Maximum Production
To encourage high fruit production, melons must be planted in the right conditions with proper spacing.
Steps to Plant Melons:
- Select a Sunny Spot: Melons need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Plant in Mounds or Raised Beds: This improves drainage and warms the soil faster.
- Sow Seeds Directly: Plant 2-3 seeds per hole, 1 inch deep.
- Thin Seedlings: Once plants are 3 inches tall, remove weaker seedlings, keeping the strongest.
- Spacing: Keep plants 2-3 feet apart to allow vine growth and airflow.
4. Watering Techniques for Better Fruit Development
Melons need consistent moisture but should never be overwatered.
Watering Guidelines:
- Water deeply 2-3 times per week to encourage deep root growth.
- Use Drip Irrigation or Soaker Hoses to keep soil moist without wetting leaves.
- Reduce watering once fruits start developing to enhance sweetness.
Mulch around plants with straw or wood chips to retain moisture and prevent weeds.
5. Fertilization – The Key to Continuous Fruiting
Providing the right nutrients at different growth stages ensures strong vines and abundant fruiting.
Best Fertilizers for Melons:
- Nitrogen-Rich Fertilizer (Early Stage): Apply compost tea or fish emulsion to promote vine growth.
- Balanced Fertilizer (After Flowering): Use a 10-10-10 NPK formula to support fruit development.
- Potassium and Phosphorus Boost (Fruit Ripening): Wood ash or banana peel tea enhances fruit sweetness.
- Epsom Salt (Magnesium Source): A tablespoon per gallon of water prevents leaf yellowing and supports flowering.
6. Supporting Melon Vines for Higher Yields
Properly training and supporting melon vines helps increase fruit production and prevents rot.
Effective Training Techniques:
- Use Trellises or Cages: Vertical growth increases airflow and prevents disease.
- Tie Vines Gently: Use soft ties or clips to secure vines to supports.
- Provide Fruit Slings: Support heavy fruits with fabric slings to prevent breakage.
- Prune Excess Growth: Remove weak or excess vines to direct energy to fruit development.
7. Boosting Pollination for More Fruits
Poor pollination is a common reason for low fruit production. Enhancing pollination will lead to a higher yield.
How to Improve Pollination:
- Attract Pollinators: Plant companion flowers like marigolds, lavender, or sunflowers nearby.
- Hand-Pollinate: Use a small brush to transfer pollen from male to female flowers.
- Avoid Pesticides: Harmful chemicals can reduce bee populations and hinder pollination.
8. Preventing Common Melon Pests and Diseases
Keeping your melon plants healthy ensures a high yield and prevents crop loss.
Common Pests & Organic Solutions:
- Aphids & Spider Mites: Spray neem oil or insecticidal soap.
- Squash Bugs & Cucumber Beetles: Use floating row covers and handpick bugs.
- Powdery Mildew & Fungal Infections: Ensure proper spacing and apply a baking soda spray.
9. Harvesting Melons at the Right Time
Knowing when to harvest melons ensures they are at peak sweetness and quality.
Signs of Ripe Melons:
- Cantaloupe: The skin turns golden, and a sweet aroma develops.
- Watermelon: The tendril closest to the fruit turns brown, and the underside turns yellow.
- Honeydew: The skin becomes slightly soft, and the fruit slips off the vine with light pressure.
Harvesting Tips:
- Use sharp scissors or pruners to cut melons cleanly from the vine.
- Store at room temperature for 1-2 days to enhance sweetness.
- Refrigerate for up to 2 weeks or freeze melon cubes for smoothies.
10. Succession Planting for Continuous Melon Harvests
To enjoy melons throughout the season, plan for continuous planting.
- Sow new seeds every 3-4 weeks to maintain a steady supply.
- Rotate melon crops with beans or leafy greens to replenish soil nutrients.
- Refresh soil with compost between planting cycles for healthy growth.
Conclusion
With the right techniques, growing melons with an abundant harvest is easy and rewarding. By selecting high-yield varieties, optimizing soil conditions, ensuring proper pollination, and providing the necessary support and care, you can enjoy a continuous supply of delicious melons all season long. Whether you have a backyard garden, a terrace, or a small urban space, these tips will help you maximize your melon production. Start planting today and get ready for an explosion of juicy, homegrown melons!